
Your success in is our sole target and we develop all our in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. for Oracle 1Z0-821 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Also have 1Z0-821 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
User jack logs in to host solar in and issues the following command:
jack@solaris:-$ ls .ssh
id_dsa id_dsa.pub id_rsa id_rsa.pub known_hosts authorized_keys Which two are true?
Answer: AE
Explanation: A: You will see two files starting with id_rsa. id_rsa is the private key and id_rsa.pub is public key.
E: The .ssh/known_hosts file
In order to use public-key secure connection with other hosts (ssh, scp, sftp) there is a special directory, ~/.ssh/, where passphrases and public keys are stored. Normally you wouldn't need to know the gory details, but from time to time a host will change its public key and then you have difficulty using ssh or scp with that host, and have to edit a file named known_hosts.
If you try to ssh to another computer, but get an error message that warns about a changed or incorrect public key, then it is probably just a case of that host changing its public key. (It is possible, though usually not the case, that malicious hacking is involved.) Unless you actually suspect hacker involvement, you can edit the file ~/.ssh/known_hosts using your usual text editor (vi, emacs, nedit, or pico) and delete any line with the name of that host.
Then when you try to ssh that host again, it will be like the first time ever; ssh will ask you if you want to accept a new public key, you type the whole word yes, and everything will proceed normally from there.
Here is what a typical ~/.ssh/known_hosts file might contain. Note that newton is represented on two different lines:
newton 1024 35
153438062610297067329638677441205712613292203533062535600064224677647442
245028855505387934431717435134842994423656065076260604296084868001730665
553662299156116414854701274715680961503198280525759778667306417179500370
189017139564144825610347509023078143132936185076849630461827976942220442
313116255293297021841
ucsub 1024 37
132170811640421742212085598383135714069016332111955003414250071326834884
018721183646445780180633494496866895830879394309011412231102757022090299
732775466435482517698989962531081214859205054227533597152962802400251809
883548442498002326460312850336779152617243800769119880843882425555806081
435017335194477605333
simpson 1024 41
840896920592494584403453622735282634536002054701576247765078766974814128
393752943151071629834843909016027026612791643752972116459602750267266908
365259665072736159491719667576217171370458928680504368847255632477925660
234893185547218857655484574619075125368470792976275806263534208879722192
77539015703446529603
newton, 128.138.249.8 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAIEA0d7Aoure0toNJ+YMYi61QP2ka8m5x5ZQlT7obP8C
K3eropfqsMPPY6uiyIh9vpiFX2r1LHcbx139+vG6HOtVvuS8+IfMDtawm3WQvRuOopz3vVy 5GtMwtaOgehsXoT930Ryev1bH5myPtWKlipITsOd2sX9k3tvjrmme4KCGGss=
NEW QUESTION 2
You have installed an update to the gzip package and need to "undo" .ho update and return the package to its "as-delivered" condition. Which command would you use?
Answer: B
Explanation: Use the pkg revert command to restore files to their as-delivered condition.
NEW QUESTION 3
You are attempting to edit your crontab file in the bash shell. Instead of getting your usual vi interface, you are presented with an unfamiliar interface. In order to have your editor of choice-vi- what command must you type after exiting the unfamiliar editor?
Answer: A
Explanation: Set the EDITOR variable to vi.
Commands like `crontab -e` will use ed per default. If you'd like to use some better editor (like vi) you can use the environment variable EDITOR:
# EDITOR=vi; crontab –e will open the users crontab in vi. Of course you can set this variable permanently.
Incorrect answers
C: -e Edits a copy of the current user's crontab file, or creates an empty file to edit if crontab does not exist. When editing is complete, the file is installed as the user's crontab file. If a username is given, the specified user's crontab file is edited, rather than the current user's crontab file; this can only be done by a user with the solaris.jobs.admin authorization. The environment variable EDITOR determines which editor is invoked with the -e option. The default editor is ed(1). All crontab jobs should be submitted using crontab. Do not add jobs by just editing the crontab file, because cron is not aware of changes made this way.
NEW QUESTION 4
Which two statements are true concerning the network stack on Oracle Solaris 11?
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 5
The crash dump notification on your server is:
Documentation states that there should be two core files for each crash dump in the
/var/crash directory named vmdump.0
Which command should you choose to display theses two files?
Answer: A
Explanation: Decompress using savecore -f vmdump.0
savecore - save a crash dump of the operating system
-f dumpfile Attempt to save a crash dump from the specified file instead of from the system's current dump device. This option may be useful if the information stored on the dump device has been copied to an on-disk file by means of the dd(1M) command.
NEW QUESTION 6
You want to delete the IPv4 address on the interface net3. Which command should you use?
Answer: E
Explanation: The ipadm delete-addr subcommand removes addresses from interfaces. To remove an address from the IPMP group, type the following command:
# ipadm delete-addr addrobj
The addrobj uses the naming convention inder-interface/user-string.
NEW QUESTION 7
You have installed the SMF notification framework to monitor services. Which command is used to set up the notifications for a particular service?
Answer: A
Explanation: How to Set Up Email Notification of SMF Transition Events
This procedure causes the system to generate an email notification each time one of the services or a selected service has a change in state. You can choose to use either SMTP or SNMP. Normally, you would only select SNMP if you already have SNMP configured for some other reason.
By default, SNMP traps are sent on maintenance transitions. If you use SNMP for monitoring, you can configure additional traps for other state transitions.
1. Become an administrator or assume a role that includes the Service Management rights profile.'
2. Set notification parameters. Example 1:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when transactions go into the maintenance state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg setnotify -g maintenance mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Example 2:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when the switch service goes into the online state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg -s svc:/system/name-service/switch:default setnotify to-online mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Note: The svccfg command manipulates data in the service configuration repository. svccfg can be invoked interactively, with an individual subcommand, or by specifying a command file that contains a series of subcommands.
Changes made to an existing service in the repository typically do not take effect for that service until the next time the service instance is refreshed.
NEW QUESTION 8
You are the administrator of a system that a large number of developers work on. These developers crash the system, and their applications, on a regular basis.
What command would you use to configure where the core files are saved?
Answer: E
Explanation: The coreadm command is used to specify the name and location of core files produced by abnormally-terminating processes.
NEW QUESTION 9
United States of America export laws include restrictions on cryptography.
Identify the two methods with which these restrictions are accommodated in the Oracle Solaris 11 Cryptographic Framework.
Answer: BC
Explanation: B: Binary Signatures for Third-Party Software
The elfsign command provides a means to sign providers to be used with the Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework. Typically, this command is run by the developer of a provider.
The elfsign command has subcommands to request a certificate from Sun and to sign binaries. Another subcommand verifies the signature. Unsigned binaries cannot be used by the Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework. To sign one or more providers requires the certificate from Sun and the private key that was used to request the certificate.
C: Export law in the United States requires that the use of open cryptographic interfaces be restricted. The Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework satisfies the current law by requiring that kernel cryptographic providers and PKCS #11 cryptographic providers be signed.
NEW QUESTION 10
Your mentor suggests using the dladm rename-link command to rename the network datalinks.
What are the two advantages of following this advice?
Answer: AD
Explanation: Note: dladm rename-link [-R root-dir] link new-link
Rename link to new-link. This is used to give a link a meaningful name, or to associate existing link configuration such as link properties of a removed device with a new device.
NEW QUESTION 11
alice is a user account used by Alice on a Solaris 11 system. sadmin is a role account on the same system.
Your task is to add the command /usr/sbin/cryptoadm to the Network management profile, so that Alice can execute it, while assuming the sadmin role.
Select the three activities necessary to accomplish this.
Answer: CDG
Explanation: C: /etc/security/exec_attr is a local database that specifies the execution attributes associated with profiles. The exec_attr file can be used with other sources for execution profiles, including the exec_attr NIS map and NIS+ table.
A profile is a logical grouping of authorizations and commands that is interpreted by a profile shell to form a secure execution environment.
NEW QUESTION 12
You want to deploy Oracle Solaris 11 with the Automated Installer (AI). You need to make sure that your server and network meet the requirements for using AI.
Identify two requirements for using AI.
Answer: AD
Explanation: A: An automated installation of a client over the network consists of the following high-level steps:
Step 1. The client system boots over the network and gets its network configuration and the location of the install server from the DHCP server.
Step 2: The install server provides a boot image to the client. Etc.
D: If two client machines need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS but need to be installed differently in other ways, then create two AI manifests for the AI install service. The different AI manifests can specify different packages to install or a different slice as the install target, for example.
NEW QUESTION 13
Identify the correct description of an IPS image.
Answer: D
Explanation: An image is a location where packages can be installed. An image can be one of three types:
* Full images are capable of providing a complete system.
* Partial images are linked to a full image (the parent image), but do not provide a complete system on their own.
* User images contain only relocatable packages.
NEW QUESTION 14
Which modification needs to be made to the Service Management Facility before you publish a new package to the IPS repository?
Answer: D
Explanation: pkg/image_root
(astring) The path to the image whose file information will be used as a cache for file data.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two are user definable OpenBoot parameters that can be set in the OpenBoot PROM?
Answer: DE
Explanation: The NVRAM chip stores user-definable system parameters, also referred to as NVRAM variables or EEPROM parameters. The parameters allow administrators to control
variables such as the default boot device and boot command. The NVRAM also contains writeable areas for user-controlled diagnostics, macros, and device aliases. NVRAM is where the system identification information is stored, such as the host ID, Ethernet address, and time-of-day (TOD) clock.
Examples of NVRAM variables:
Variable Default Description boot-device disk or net The device from which to start up.
diag-device net The diagnostic startup source device.
diag-file Empty string Arguments passed to the startup program in diagnostic mode. diag-switch? false Whether to run in diagnostic mode
NEW QUESTION 16
Which network protocol provides connectionless, packet-oriented communication between applications?
Answer: B
Explanation: The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network without requiring prior communications to set up special transmission channels or data paths.
Compared to TCP, UDP is a simpler message-based connectionless protocol.
NEW QUESTION 17
Consider the following commands: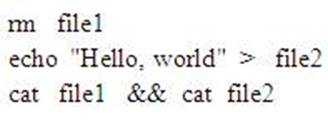
What is displayed when this sequence of commands is executed using the bash shell?
Answer: B
Explanation: First line (rm file1) deletes/removes file1. Second line captures the text into file2.
The first part of line 3 (cat file1) fails as the file1 does not exist.
The && (AND) operator will ensure that the third line fails. The result of line 3 will be the result of first part of line 3 (cat file1).
Note: cat - concatenate files and print on the standard output
Note #1: A list is a sequence of one or more pipelines separated by one of the operators ‘;’, ‘&’, ‘&&’, or ‘||’, and optionally terminated by one of ‘;’, ‘&’, or a newline.
Of these list operators, ‘&&’ and ‘||’ have equal precedence, followed by ‘;’ and ‘&’, which have equal precedence.
AND and OR lists are sequences of one or more pipelines separated by the control operators ‘&&’ and ‘||’, respectively. AND and OR lists are executed with left associativity.
An AND list has the form command1 && command2
command2 is executed if, and only if, command1 returns an exit status of zero.
An OR list has the form command1 || command2
command2 is executed if, and only if, command1 returns a non-zero exit status.
The return status of AND and OR lists is the exit status of the last command executed in the list.
Note #2 (on exit status): Zero means command executed successfully, if exit status returns non-zero value then your command failed to execute.
NEW QUESTION 18
You have been asked to terminate a process that appears to be hung and will not terminate. The process table is shown below:
root 15163 15156 0 12:51:15 pts/3 0:00 hungscript What command will terminate the process?
Answer: A
Explanation: Here we should use SIGTERM to terminate the process. Note:
When no signal is included in the kill command-line syntax, the default signal that is used is
–15 (SIGKILL). Using the –9 signal (SIGTERM) with the kill command ensures that the process terminates promptly. However, the –9 signal should not be used to kill certain processes, such as a database process, or an LDAP server process. The result is that data might be lost.
Tip - When using the kill command to stop a process, first try using the command by itself, without including a signal option. Wait a few minutes to see if the process terminates before
using the kill command with the -9 signal.
NEW QUESTION 19
You suspect a problem with the oponldap package and want to make sure that the files have not be modified or otherwise tampered with.
Which command would validate all of the files contained in the openldap package and report any problems?
Answer: A
Explanation: pkgchk checks the accuracy of installed files or, by using the -l option, displays information about package files. pkgchk checks the integrity of directory structures and files. Discrepancies are written to standard error along with a detailed explanation of the problem.
Thanks for reading the newest 1Z0-821 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Passcertsure 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.passcertsure.com/1Z0-821-test/ (243 Q&As Dumps)