- Home
- Cisco
- 642-885 Exam
Cisco 642-885 Free Practice Questions
Our pass rate is high to 98.9% and the similarity percentage between our 642-885 study guide and real exam is 90% based on our seven-year educating experience. Do you want achievements in the Cisco 642-885 exam in just one try? I am currently studying for the Cisco 642-885 exam. Latest Cisco 642-885 Test exam practice questions and answers, Try Cisco 642-885 Brain Dumps First.
Free demo questions for Cisco 642-885 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
A network engineer must configure a Cisco IOS XR router with BGP dampening. Which configuration meets these parameters?
- A. router bgp 60 bgp dampening
- B. router bgp 60 neighbor 10.0.0.2 bgp dampening
- C. router bgp 60address-family ipv4 unicast bgp dampening
- D. route-policy dampening_specific drop!router bgp 60address-family ipv4 unicastbgp dampening route-policy dampening_specific
- E. router bgp 60 address-family ipv4 bgp dampening
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 2
Which difference occurs between intradomain and interdomain routing technology?
- A. PIM is used in intradomain routing technology and uses reverse path forwarding mechanism to implement optimize multicast data forwarding.
- B. MSDP is used in intradomain routing technology to discover the multicast source.
- C. Interdomain routing technology uses MSDP and M-BGP for exchanging multicast routing information.
- D. RP is not needed in intradomain routing technology, but RP is needed in interdomain routing technology to receive multicast traffic.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 3
When implementing high-availability stateful switchover BGP routing, in which situation would Cisco NSR be required?
- A. On the PE routers connecting to the CE routers which are not NSF aware or are not NSF capable
- B. On the PE routers connecting to the CE routers which support graceful restart
- C. On the PE routers connecting to the CE routers which are incapable of performing stateful switchover operations because the CE routers are only NSF aware but not NSF capable
- D. On the PE routers connecting to the CE routers which are incapable of performingstateful switchover operations because the CE routers are only NSF capable but not NSF aware
- E. On the service provider core P routers which are also NSF aware
- F. On the service provider core P routers which are also NSF capable
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 4
Which four statements are correct regarding MSDP configurations and operations? (Choose four.)
- A. The MSDP peers are also typically the RPs in respective routing domains.
- B. SA messages are flooded to all other MSDP peers without any restrictions
- C. On Cisco IOS, IOS-XE, and IOS-XR, the router can be configured to cache the SA messages to reduce the join latency
- D. SA messages are used to advertise active sources in a domain
- E. MSDP establishes neighbor relationships with other MSDP peers using TCP port 639
- F. MSDP peerings on Cisco IOS, IOS-XE, and IOS-XR support MD5 or SHA1 authentication
Answer: ACDE
NEW QUESTION 5
An SP core is running PIM on the network. Multicast groups in this networkare in the 232.0.0.0/8 range. Which commandenables multicast routing operations without using an RP?
- A. ip pim autorp
- B. ip pim ssm default
- C. ip pim bidir-enable
- D. ip pim register-source
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 6
Which two features are used to provide high availability multicast? (Choose two.)
- A. BFD
- B. NSF/SSO
- C. PIM NSR
- D. PIM triggered join
- E. IGMP triggered report
- F. MSDP
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Triggered joins are sent when the primary or the secondary RPF information changes. No RPF change prunes are sent for MoFRR streams.
mofrr
To perform a fast convergence (multicast-only fast reroute, or MoFRR) of specified routes/flows when a failure is detected on one of multiple equal-cost paths between the router and the source, use the mofrr command under PIM configuration mode.
mofrr rib acl_name no rib acl_name
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.

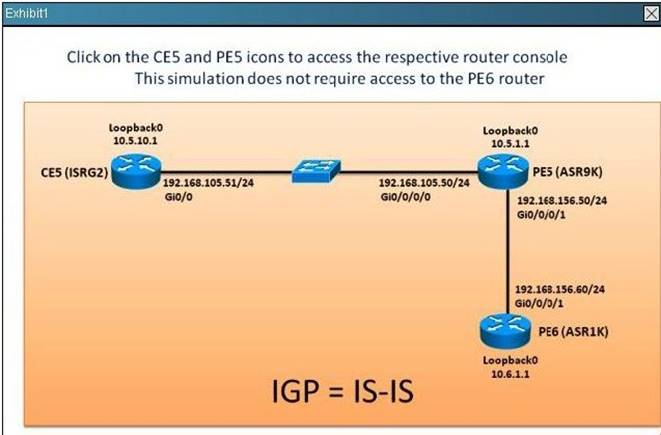
On the PE, which two statements are correct regarding the(192.168.156.60,224.1.1.1) entry? (Choose two,)
- A. The RPF neighbor points towards the RP
- B. The RPF neighbor is reachable overthe Gi0/0/0/1 interface
- C. The OIL contains the GiO/0/0/0 interface
- D. The IIL is Null
Answer: AC
Explanation:
#show ip mroute
NEW QUESTION 8
Which configuration would an engineer use to exchange IPv6 multicast routes via BGP with a neighbor that does not support thecorresponding Multicast SAFI onCisco IOS XE?
- A. router bgp 100bgp router-id 209.165.201.10 no bgp default ipv4-unicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 remote-as 201neighbor 2001:DB8::10 update-source GigabitEthernet 0/10 address-family ipv6 multicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 activate network 2001:DB8:CDCD:1::/64exit-address-family
- B. router bgp 100bgp router-id 209.165.201.10 no bgp default ipv4-unicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 remote-as 201neighbor 2001:DB8::10 update-source GigabitEthernet 0/10 address-family ipv6neighbor 2001:DB8::10 translate-update ipv6 multicast unicast neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activateno synchronization exit address-familyaddress-family ipv6 multicast neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activate network 2001:DB8:CDCD:1::/64exit-address-family
- C. router bgp 100bgp router-id 209.165.201.10 no bgp default ipv4-unicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 remote-as 201neighbor 2001:DB8::10 update-source GigabitEthernet 0/10 address-family ipv6neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activate address-family ipv6 multicast neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activate network 2001:DB8:CDCD:1::/64exit-address-family
- D. router bgp 100bgp router-id 209.165.201.10 no bgp default ipv4-unicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 remote-as 201neighbor 2001:DB8::10 update-source GigabitEthernet 0/10 address-family ipv6neighbor 2001:DB8::10 translate-update ipv6 multicast unicast no synchronizationexit address-familyaddress-family ipv6 multicast neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activate network 2001:DB8:CDCD:1::/64exit-address-family
- E. router bgp 100bgp router-id 209.165.201.10 no bgp default ipv4-unicastneighbor 2001:DB8::10 remote-as 201neighbor 2001:DB8::10 update-source GigabitEthernet 0/10 address-family ipv6neighbor 2001:DB8::10 send-labelneighbor 2001:DB8::10 override-capability-neg neighbor 2001:DB8::10 activateno synchronization exit address-familyaddress-family ipv6 multicast network 2001:DB8:CDCD:1::/64exit-address-family
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 9
Referring to the topology diagram show in the exhibit,
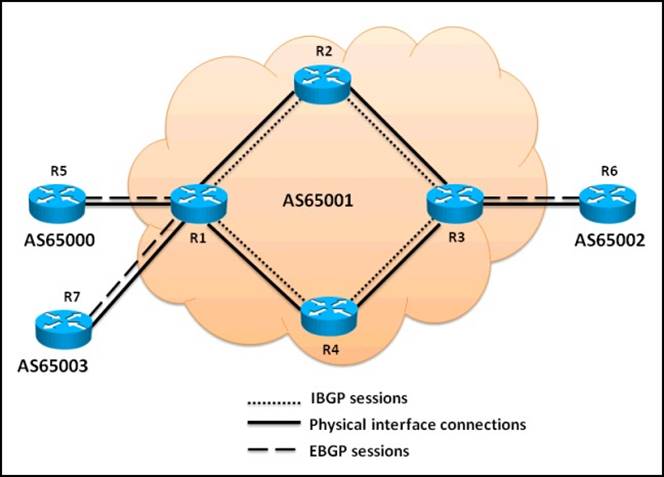
which three statements are correct regarding the BGP routing updates? (Choose three.)
- A. The EBGP routing updates received by R1 from R5 will be propagated to the R2, R4, and R7 routers
- B. The EBGP routing updates received by R3 from R6 will be propagated to the R2 and R4 routers
- C. The EBGP routing updates received by R1 from R5 will be propagated to the R2 and R4 routers
- D. The IBGP routing updates received by R3 from R2 will be propagated to the R6 router
- E. The IBGP routing updates received by R2 from R1 will be propagated to the R3 router
- F. The IBGP routing updates received by R1 from R4 will be propagated to the R5, R7, and R2 routers
Answer: ABD
NEW QUESTION 10
Which of the following can be used by dual-stack service providers supporting IPv4/IPv6
customers with dual-stack hosts using public IPv6 addresses and private IPv4 addresses?
- A. NAT64
- B. 6RD
- C. 6to4 tunnels
- D. Carrier-grade NAT
Answer: D
Explanation:
Carrier Grade NAT is a large-scale NAT, capable of providing private-IPv4-to-public-IPv4 translation in the order of millions of translations. Carrier Grade NAT can support several hundred thousand subscribers with the bandwidth throughput of at least 10Gb/s full-duplex. With IPv4 addresses reaching depletion, Carrier Grade NAT is vital in providing private IPv4 connectivity to the public IPv4 internet. In addition, Carrier Grade NAT is not limited to IPv4 NAT; it can also translate between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which technology is categorized as multicast ASM and multicast SSM?
- A. IP telephony
- B. video conferencing
- C. IPTV
- D. live streaming
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 12
Which configuration for implementing 6PE on an IS-IS-enabled Cisco IOS XR router is correct?
- A. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:DD11::1/64 router isis ipv6-tunnet 49.0000.0000.00010.00address-family ipv6 unicast single-topologyredistribute bgp 200interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 address-family ipv6 unicast router bgp 200bgp router-id 209.165.202.129 address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute isis ipv6-tun neighbor 209.165.202.130remote-as 200address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast
- B. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:DD11::1/64 router isis ipv6-tunnet 49.0000.0000.00010.00address-family ipv6 unicast single-topologyrouter bgp 200bgp router-id 209.165.202.129 address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute isis ipv6-tun neighbor 209.165.202.130remote-as 200address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast
- C. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:DD11::1/64 router isis ipv6-tunnet 49.0000.0000.00010.00address-family ipv6 unicast single-topologyinterface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 address-family ipv6 unicast router bgp 200bgp router-id 209.165.202.129 address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute staticneighbor 209.165.202.130remote-as 200address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast
- D. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:DD11::1/64 router isis ipv6-tunnet 49.0000.0000.00010.00address-family ipv6 unicast single-topologyinterface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 address-family ipv6 unicast router bgp 200bgp router-id 209.165.202.129 address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 unicastredistribute connected redistribute isis ipv6-tun neighbor 209.165.202.130remote-as 200address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast
- E. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:DD11::1/64 router isis ipv6-tunnet 49.0000.0000.00010.00address-family ipv6 unicast single-topologyinterface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 address-family ipv6 unicast router bgp 200bgp router-id 209.165.202.129 address-family ipv4 unicast address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute connected redistribute isis ipv6-tun neighbor 209.165.202.130remote-as 200address-family ipv4 unicast
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 13
Assume that the R1 router is enabled for PIM-SM and receives a multicast packet sourced from 172.16.1.100, and the R1 router has multicast receivers on the Gi0/1, Gi0/2, Gi0/3 and Gi0/4 interfaces.
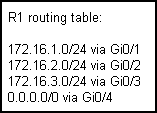
The multicast packet from the 172.16.1.100 source must arrive on which interface on the R1 router for it to be forwarded out the other interfaces?
- A. Gi0/1
- B. Gi0/2
- C. Gi0/3
- D. Gi0/4
- E. Gi0/1 or Gi0/2 or Gi0/3 or Gi0/4
- F. Gi0/2 or Gi0/3
- G. Gi0/1 or Gi0/4
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 14
Which two options areadvantages of an IPv6 dual-stack implementation in an enterprise environment? (Choose two.)
- A. simplifies the route redistribution policies complexity
- B. requires IPv6-to-IPv4 translation on the uplinks to the service providers
- C. provides built-in support for Kerberos authentication
- D. does not have to worry about NAT traversal
- E. supports multicast properly
Answer: DE
NEW QUESTION 15
The 224.192.16.1 multicast IP address maps to which multicast MAC address?
- A. 01-00-5E-C0-10-01
- B. 01-00-5E-40-10-01
- C. 01-00-5E-00-10-01
- D. 01-00-5E-C0-16-01
Answer: B
Explanation:
Least significant 23 bits of IP address and pre-pend 01-00-5E
224 ignore
192 less 128 becomes 64 = 40
16 = 10
1 = 01
01-00-5E-40-10-01
NEW QUESTION 16
Which command set implements BGP support for NSF/SSO on Cisco IOS XE between a PE and a route reflector?
- A. On RR:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesbgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 bgp graceful-restartneighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 200neighbor 10.20.20.2 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.2 activateneighbor 10.20.20.2 send-community both neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-reflector-client exit-address-familyOn PE:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesbgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 bgp graceful-restartneighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 300neighbor 10.20.20.1 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.1 activateneighbor 10.20.20.1 send-community both exit-address-family!
- B. On RR:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesbgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 bgp graceful-restartneighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 200neighbor 10.20.20.2 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.2 activateneighbor 10.20.20.2 send-community both neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-reflector-client exit-address-familyOn PE:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.20.02.1 remote-as 300neighbor 10.20.20.1 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.1 activateneighbor 10.20.20.1 send-community both exit-address-family!
- C. On RR:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesbgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 bgp graceful-restartneighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 200neighbor 10.20.20.2 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.2 activateneighbor 10.20.20.2 send-community both neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-reflector-client exit-address-familyOn PE:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 300neighbor 10.20.20.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.20.20.1 ha-mode ssono auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.1 activateneighbor 10.20.20.1 send-community both exit-address-family!
- D. On RR:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 200neighbor 10.20.20.2 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.20.20.2 ha-mode ssono auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.2 activateneighbor 10.20.20.2 send-community both neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-reflector-client exit-address-familyOn PE:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 300neighbor 10.20.20.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.20.20.1 ha-mode ssono auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.1 activateneighbor 10.20.20.1 send-community both exit-address-family!
- E. On RR:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 10.20.20.2 remote-as 200neighbor 10.20.20.2 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.2 activateneighbor 10.20.20.2 send-community both neighbor 10.20.20.2 route-reflector-client exit-address-familyOn PE:router bgp 300no synchronizationbgp log-neighbor-changesbgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 bgp graceful-restartneighbor 10.20.20.1 remote-as 300neighbor 10.20.20.1 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary!address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.20.20.1 activateneighbor 10.20.20.1 send-community both exit-address-family!
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 17
Which command configures a Source Specific Multicast on a Cisco IOS XR router?
- A. configuremulticast-routing address-family ipv4 interface all enableexitrouter igmp version 3 commit
- B. configuremulticast-routing address-family ipv4 interface all enableexitrouter igmp version 2 commit
- C. configuremulticast-routing address-family ipv4 interface all enableexitrouter igmp version 1commit
- D. configure interface all enable exitrouter igmp version 3 commit
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 18
Refer to the exhibit.

Which configuration is missing to complete the configuration task of enabling BFD with the 192.168.1.1 EBGP peer?
- A. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled globally under router bgp 64500 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp)#bfd fast-detect
- B. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the address-family under address-family ipv4 unicastRP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-af)#bfd fast-detect
- C. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the 192.168.1.1 neighbor under neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-nbr)#bfd fast-detect
- D. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the 192.168.1.1 neighbor address-family under neighbor 192.168.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicastRP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-nbr-af)#bfd fast-detect
- E. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled globally on the router RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config)#bfd fast-detect
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 19
What is one of the configuration errors within an AS that can stop a Cisco IOS-XR router from announcing certain prefixes to its EBGP peers?
- A. Some prefixes were mistagged with the no-export BGP community
- B. Some prefixes were set with an MED of 0
- C. The outbound BGP route policy only has set actions defined without any pass actions defined
- D. The inbound BGP route policy only has set actions defined without any pass actions defined
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 20
With PIM-SM operations, which four pieces of information are maintained in the multicast routing table for each (*,G) or (S,G) entry? (Choose four.)
- A. RPF Neighbor
- B. RP Set
- C. Incoming Interface
- D. OIL
- E. DF priority
- F. PIM SM state flags
Answer: ACDF
Explanation:
The following is sample output from the show ip mroute command for a router operating in sparse mode:
show ip mroute
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, C - Connected, L - Local, P - Pruned R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop, State/Mode
(*, 224.0.255.3), uptime 5:29:15, RP is 198.92.37.2, flags: SC
Incoming interface: Tunnel0, RPF neighbor 10.3.35.1, Dvmrp Outgoing interface list:
Ethernet0, Forward/Sparse, 5:29:15/0:02:57
(198.92.46.0/24, 224.0.255.3), uptime 5:29:15, expires 0:02:59, flags: C
Incoming interface: Tunnel0, RPF neighbor 10.3.35.1 Outgoing interface list:
Ethernet0, Forward/Sparse, 5:29:15/0:02:57
NEW QUESTION 21
Refer to the exhibit.

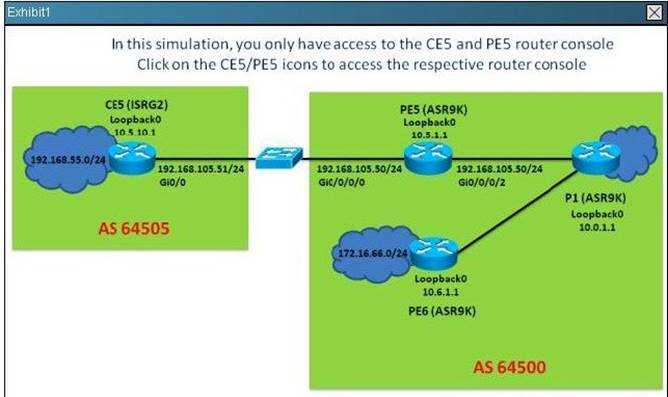
Which two statements regarding the BGP peerlngs are correct? (Choose two)
- A. On PE5,the incoming prefixes received from the 192.168.105.51 EBGP peer is limited to a maximum of 10 prefixes
- B. On PE5, the "rplin" inbound route policy is applied to the 192.168.105.51 EBGP peer
- C. On PE5, the "pass" outbound route policy is applied to the 192.168.105.51 EBGP peer
- D. PE5 has one EBGP peer (CE5) and two IBGP peers (P1 and PE6)
- E. PE5 has received a total of 60 prefixes from its neighbors
Answer: AE
Explanation:
#show ip bgp
NEW QUESTION 22
Refer to the configuration exhibit, taken from a Cisco IOS-XR router.
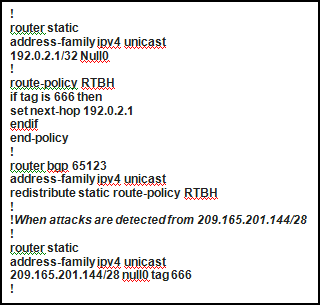
Which configuration change is required to properly enable this router as the signaling router for implementing source-based RTBH filtering?
- A. Set community (no-export) in the route policy
- B. Pass in the route policy
- C. Set local-preference 1000 in the route policy
- D. The 192.0.2.1/32 static route should be tagged as 666 (tag 666)
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 23
Which IPv6 mechanism occurs between a provider edge router and the customer premises equipment router to allow an ISP to automate the process of assigning a block of IPv6 addresses to a customer for use within the customer network?
- A. Router Advertisement
- B. DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
- C. DHCPv6 Lite
- D. Stateful DHCPv6
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk872/technologies_configuration_example09186a0080b 8a116.shtml
NEW QUESTION 24
A junior network engineer has just configured a new IBGP peering between two Cisco ASR9K PE routers in the network using the loopback interface of the router, but the IBGP neighborship is not able to be established. Which two verification steps will be helpful in troubleshooting this problem? (Choose two.)
- A. Verify that the network command under router BGP is configured correct on each router for announcing the router's loopback interface in BGP
- B. Verify that the ibgp-multihop command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router
- C. Verify that the loopback interfaces are reachable over the IGP
- D. Verify that the update-source loopback command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router
- E. Verify that the ttl-security command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router to enable the router to send the BGP packets using a proper TTL value
- F. Verify that the UDP port 179 traffic is not being blocked by an ACL or firewall between the two IBGP peers
Answer: CD
P.S. Easily pass 642-885 Exam with 131 Q&As Certstest Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Certstest 642-885 Dumps: https://www.certstest.com/dumps/642-885/ (131 New Questions)












