
Act now and download your Cisco 642-889 test today! Do not waste time for the worthless Cisco 642-889 tutorials. Download Far out Cisco Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Edge Network Services (SPEDGE) exam with real questions and answers and begin to learn Cisco 642-889 with a classic professional.
NEW QUESTION 1
When implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs with customers running OSPF as the CE-PE routing protocol, the service provider MPLS backbone looks like what to the CE routers?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 2
Which option is a valid Cisco IOS XR BGP Layer 3 IPv4 MPLS VPN configuration?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 3
Which Layer 2 encapsulations can AToM solution support with interworking IP feature enable?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 4
Which Layer 2 VPN technology is implemented over an IP core network without the need for MPLS?
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/12_3t2/feature/guide/gtl2tpv3.html#wp1040784
The Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 feature expands on Cisco support of the Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 {L2TPv3}. L2TPv3 is an Internet Engineering Task Force {IETF} l2tpext working group draft that provides several enhancements to L2TP for the capability to tunnel any Layer 2 payload over L2TP.
Specifically, L2TPv3 defines the L2TP protocol for tunneling Layer 2 payloads over an IP core network using Layer 2 virtual private networks {VPNs}. Benefits of this feature include the following:
•L2TPv3 simplifies deployment of VPNs
•L2TPv3 does not require Multiprotocol Label Switching
•L2TPv3 supports Layer 2 tunneling over IP for any payload
NEW QUESTION 5
In hierarchical VPLS implementations, which two access architectures can be used between the UPE and NPE? {Choose two.}
Answer: AD
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/metro/me3600x_3800x/software/release/12.2_52_ey/configuration/gui de/swmpls.html#wp1244272
H-VPLS uses spoke connections, usually between Layer 2 switches acting as the CE and PE devices at the service provider's point-of presence {POP}. The spoke connections can be either an IEEE 802.1Q tagged connection or an MPLS LSP.
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.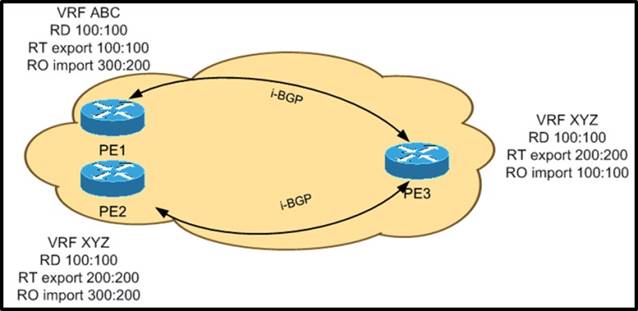
PE1 and PE2 are advertising the same subnet 10.10.10.0/24 to PE3. Which PE advertised subnet is installed at the PE3 XYZ BGP table?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 7
DRAG DROP
Answer: A
Explanation:
Business subscribers are an important segment of many service providers' customer base. The main business services that must be provided by the network today are:
• MPLS VPN
• Carrier Ethernet connectivity
• Managed services
Carrier Ethernet connectivity services have been defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum {MEF} to include ELine, E-LAN, and E-Tree service types, which are defined as follows:
• E-Line is based on a point-to-point Ethernet Virtual Connection. Two E-Line services are defined:
- Ethernet Private Line {EPL}: A very simple and basic point-to-point service characterized by low frame delay, frame delay variation, and frame loss ratio. No service multiplexing is allowed, and other than a committed information rate {CIR} no class of service {CoS} {Bandwidth Profiling} is allowed.
- Ethernet Virtual Private Line {EVPL}: A point-to-point service wherein service multiplexing {more than one Ethernet Virtual Connection} is allowed. The individual Ethernet Virtual Circuits can be defined with a rich set of Bandwidth Profiles and Layer 2 Control Protocol Processing methods as defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum.
• E-LAN is based on a multipoint-to-multipoint Ethernet Virtual Connection. Service multiplexing {more than one Ethernet Virtual Circuit at the same UNI} is permitted, as is the rich set of performance assurances defined by the MEF such as CIR with an associated Committed Burst Size {CBS} and Excess Information Rate {EIR}.
• E-Tree is a point-to-multipoint ELAN service in which the spoke "leaves" can communicate with the hub or "root" location but not with each other. Typical application for E-Tree is in franchise operations.
NEW QUESTION 8
In which configuration mode is a route distinguisher configured in a Cisco IOS XR router?
Answer: E
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.6/routing/configuration/guide/rc36book.pdf
NEW QUESTION 9
DRAG DROP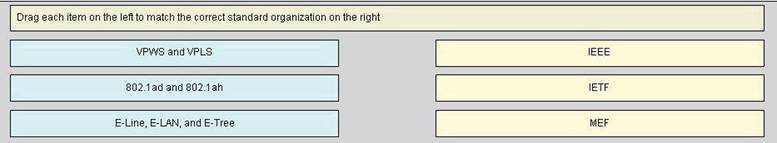
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/tech/tk891/c1482/cdccont_0900aecd80162184.pdf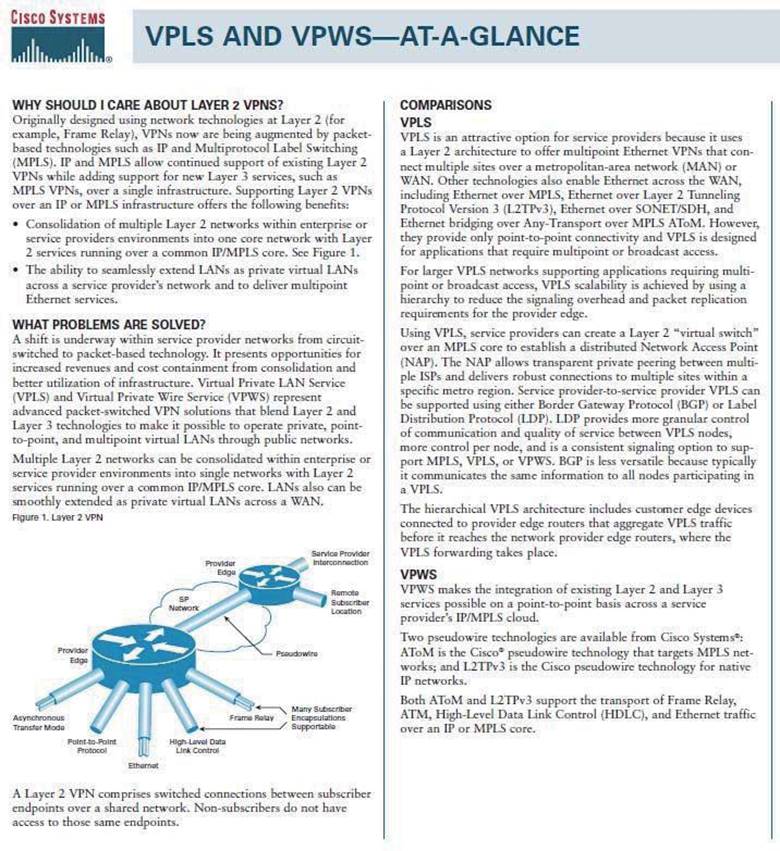
NEW QUESTION 10
In Layer 3 MPLS VPN implementations, if a customer is using the same AS number at both customer sites and the PE- to-CE routing protocol is BGP, what must be enabled on the PE router?
Answer: A
Explanation:
https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-21837
Loop prevention in BGP is done by verifying the AS number in the AS Path. If the receiving router sees its own AS number in the AS Path of the received BGP packet, the packet is dropped. The receiving Router assumes that the packet was originated from its own AS and has reached the same place from where it originated initially.
The feature could be a disaster if customers are using same AS number along the various sites and disallows customer sites having identical AS numbers to be linked by another AS number. In such a scenario, routing updates from one site will be dropped when the other site receives them.
To override this feature, AS-Override function causes to replace the AS number of originating router with the AS number of the sending BGP router. The command is neighbor ip-address as-override and can only be executed under the VPNv4 address-family
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer the exhibit.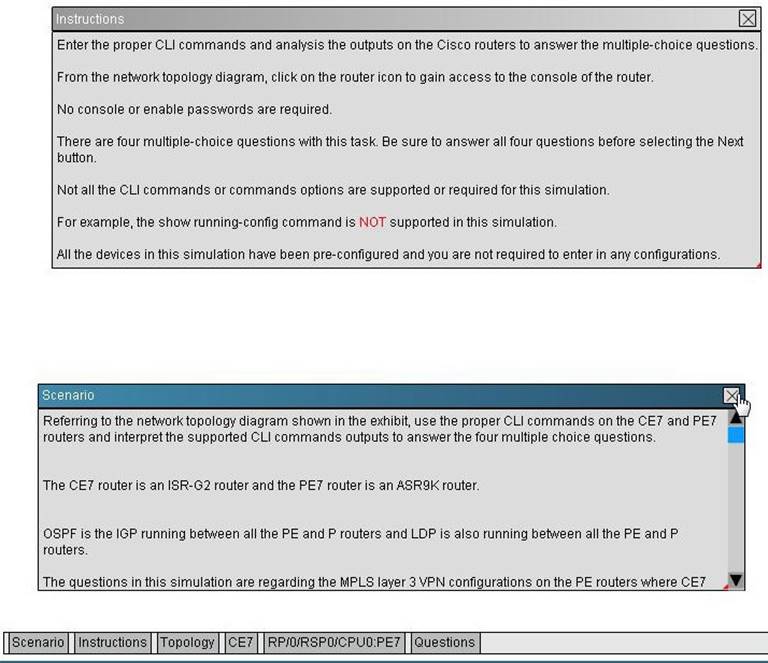
On PE7, which interface connects to the CE7 and what is the name of the VRF that interface is associated to? {Choose two.}
Answer: BC
Explanation:
# show ip vrf interfaces
NEW QUESTION 12
Refer the exhibit.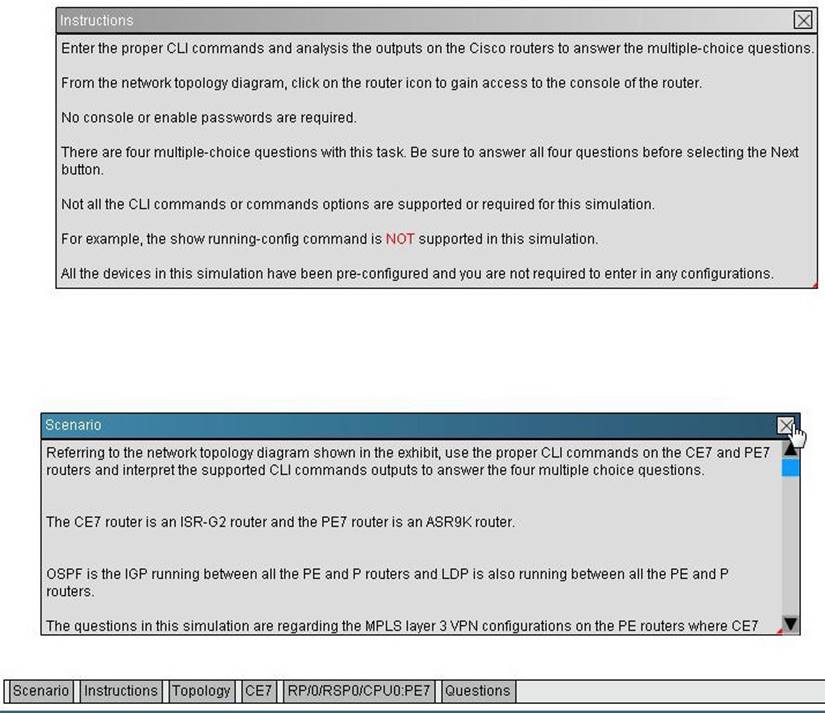
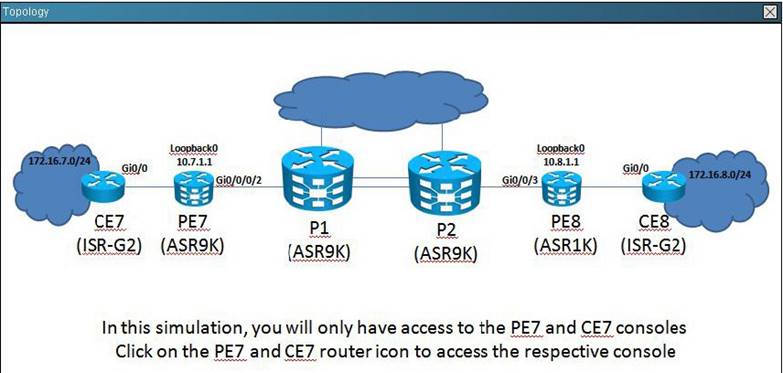
On PE7, which three statements are correct regarding the MPLS VPN configurations used to support the connectivity between the CE7 and CE8 sites? {Choose three.}
Answer: BCE
Explanation:
# show ip route show ip vrf
show ip vrf detail
NEW QUESTION 13
In MPLS Layer 3 VPN implementations, which mechanism is used to control which routes are imported to a VRF?
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://blog.initialdraft.com/archives/1537/
NEW QUESTION 14
When implementing VPLS on Cisco routers, which data structure resembles a virtual switch and is used for learning the MAC addresses?
Answer: B
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 15
DRAG DROP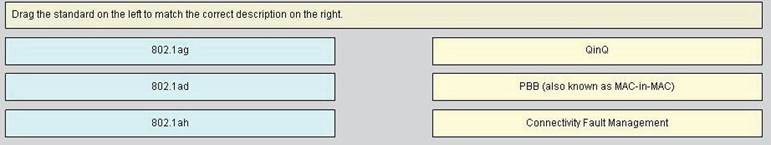
Answer: A
Explanation:
Benefits of IEEE 802.1ah standard
The benefits of IEEE 802.1ah provider backbone bridges are as follows:
• Increased service instance scalability
• MAC address scalability
IEEE 802.1ah Standard for Provider Backbone Bridging Overview
The IEEE 802.1ah Provider Backbone Bridge feature encapsulates or decapsulates end user traffic on a Backbone Edge Bridge {BEB} at the edge of the Provider Backbone Bridged Network {PBBN}. A Backbone Core Bridge {BCB} based network provides internal transport of the IEEE 802.1ah encapsulated frames within the PBBN.
Overview of OAM The advent of Ethernet as a metropolitan and wide-area networking technology has accelerated the need for a new set of OAM protocols. Service provider networks are large and complex with a wide user base, and they often involve different operators that must work together to provide end-to-end services to enterprise customers. While enterprise end-customer demands continue to increase, so do the requirements for service provider Ethernet networks, particularly in the areas of availability and mean time to repair {MTTR}. Ethernet OAM addresses these challenges and more, thereby directly impacting the competitiveness of the service provider. Ethernet has been used as a LAN technology for many years, and enterprises have managed these networks effectively, primarily with the use of Internet protocols such as Simple Network Management Protocol {SNMP}, ICMP Echo {or IP Ping}, IP Traceroute, and Cisco Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol {UDLD} and Layer 2 Traceroute
{supported in Cisco Catalyst® OS and some Cisco IOS® Software-based platforms}. In addition to these troubleshooting protocols, Cisco provides a wealth of other configuration, fault, network management, and performance management tools. Cisco also supports MPLS OAM capabilities such as Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification {VCCV} and Label Switched Path {LSP} ping on the Carrier Ethernet platforms. To complement these OAM capabilities and to ensure that Ethernet can deliver the required customer service-level agreements {SLAs}, Cisco has developed comprehensive Ethernet and IP SLA agents, along with an embedded event manager {EEM}, and IPTV video quality tools for automated measurement and troubleshooting of Carrier Ethernet deployments.
Ethernet OAM addresses the following challenges:
• The existing protocols mentioned earlier will not work unless the Ethernet layer is operating properly, making Ethernet OAM a prerequisite.
• Many service providers do not want to overlay an IP infrastructure simply for management and troubleshooting of Layer 2 Ethernet services.
• The current management protocols lack the per-customer or per-service granularity that is required to manage the individual Layer 2 Ethernet services provided to enterprises.
• The existing protocols do not assist with provisioning of Ethernet services, which is particularly difficult when the service provider and end customer must coordinate the configurations on their respective Ethernet equipment. Ethernet OAM is a broad topic, but this paper will focus on three main areas of Ethernet OAM that are most in need by service providers and are rapidly evolving in the standards bodies: Service Layer OAM {IEEE 802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management}, Link Layer OAM {IEEE 802.3ah OAM}, and Ethernet Local Management
Interface {MEF-16 E-LMI}. Each of these different OAM protocols has unique objectives and is complementary to the others IEEE 802.1ad[note 1] is an Ethernet networking standard informally known as IEEE 802.1QinQ and is an amendment to IEEE standard IEEE 802.1Q-1998. The technique is also known as provider bridging, Stacked VLANs or simply QinQ or Q-in-Q.
The original 802.1Q specification allows a single VLAN header to be inserted into an Ethernet frame. QinQ allows multiple VLAN headers to be inserted into a single frame, an essential capability for implementing Metro Ethernet network topologies. Just as QinQ extends 802.1Q, QinQ itself is extended by other Metro Ethernet protocols.[specify] In a multiple VLAN header context, out of convenience the term "VLAN tag" or just "tag" for short is often used in place of "802.1Q VLAN header". QinQ allows multiple VLAN tags in an Ethernet frame; together these tags constitute
a tag stack. When used in the context of an Ethernet frame, a QinQ frame is a frame that has 2 VLAN 802.1Q headers {double-tagged}.
There is a mild confusion regarding the naming because the 802.1ad standard was grown out of the 802.1QinQ protocol {which was developed based the trademarked method 802.1Q, with capital "Q" as a distinction instead of the 802.1q as the standardised protocol} which originally used 0x9100 as ethernet type instead of 0x88a8. While the network industry usually mix the naming the proper, standardised name is 802.1ad which sometimes gets appended by the other alternative names mentioned above; the plain "802.1QinQ" name usually refers to the old standard which is now considered obsolete
NEW QUESTION 16
Which protocol is used to hide customer VLANs inside the provider backbone network?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 17
Which option is the minimal configuration required inside the L2VPN section of a Cisco IOS XR PE router to activate VPLS functionality?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 18
With Layer 3 MPLS VPN implementations on Cisco IOS XR PE routers, an interface is assigned to a VRF using the vrf command in which configuration mode?
Answer: B
Explanation: 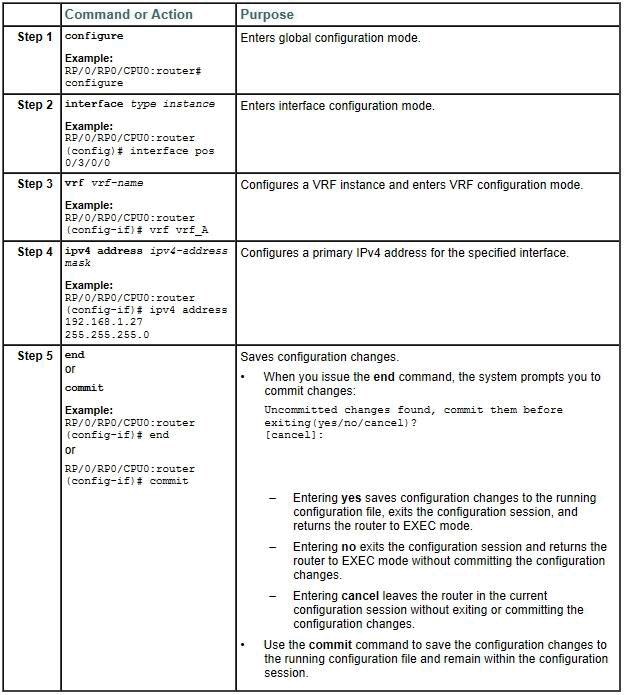
NEW QUESTION 19
When implementing H-VPLS with QinQ access on Cisco Metro Ethernet switches, which two commands enable the QinQ tagging? {Choose two.}
Answer: CE
NEW QUESTION 20
An engineer is deploying L2VPN service between two different Layer 2 encapsulations. Which feature should be set up to accomplish this task?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 21
A Cisco IOS XR device is acting as a PE. It must have an iBGP VPNv4 session with the other PE 2.2.2.2 using source loopback 0. Which configuration achieves this goal?
A}
B}
C}
D}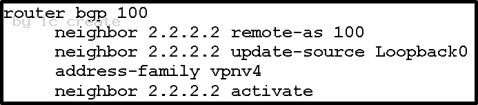
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 22
......
100% Valid and Newest Version 642-889 Questions & Answers shared by prep-labs.com, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/{productsort}/ (New 126 Q&As)