
Exam Code: GSNA (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: GIAC Systems and Network Auditor
Certification Provider: GIAC
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass GSNA Exam.
Online GSNA free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Sam works as a Network Administrator for Blue Well Inc. All client computers in the company run the Windows Vista operating. Sam creates a new user account. He wants to create a temporary password for the new user such that the user is forced to change his password when he logs on for the first time. Which of the following options will he choose to accomplish the task?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Enabling the user must change password at next logon option will make the given password a temporary password. Enabling this option forces a user to change his existing password at next logon. Answer B is incorrect. There is no such option in Windows Vist Answer D is incorrect. This option sets the password to never expire. Answer A is incorrect. This option sets the existing password as a permanent password for the user. Only administrators can change the password of the user.
NEW QUESTION 2
John works as a Network Administrator for Perfect Solutions Inc. The company has a
Linux-based network. John is working as a root user on the Linux operating system. He has recently backed up his entire Linux hard drive into the my_backup.tgz file. The size of the my_backup.tgz file is 800MB. Now, he wants to break this file into two files in which the size of the first file named my_backup.tgz.aa should be 600MB and that of the second file named my_backup.tgz.ab should be 200MB. Which of the following commands will John use to accomplish his task?
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the scenario, John wants to break the my_backup.tgz file into two files in which the size of the first file named my_backup.tgz.aa should be 600MB and that of the second file named my_backup.tgz.ab should be 200MB. Hence, he will use the the split --verbose -b 600 my_backup.tgz my_backup.tgz. command, which will automatically break the first file into 600MB named my_backup.tgz.aa, and the rest of the data (200MB) will be assigned to the second file named my_backup.tgz.ab. The reason behind the names is that the split command provides suffixes as 'aa', 'ab', 'ac', ..., 'az', 'ba', 'bb', etc. in the broken file names by default. Hence, both conditions, the file names as well as the file sizes, match with this command. Note: If the size of the tar file my_backup.tgz is 1300MB, the command split --verbose -b 600 my_backup.tgz my_backup.tgz. breaks the my_backup.tgz file into three files, i.e., my_backup.tgz.aa of size 600MB, my_backup.tgz.ab of size 600MB, and my_backup.tgz.ac of size 100MB.
NEW QUESTION 3
In which of the following social engineering attacks does an attacker first damage any part
of the target's equipment and then advertise himself as an authorized person who can help fix the problem.
Answer: A
Explanation:
A reverse social engineering attack is a person-to-person attack in which an attacker convinces the target that he or she has a problem or might have a certain problem in the future and that he, the attacker, is ready to help solve the problem. Reverse social engineering is performed through the following steps: An attacker first damages the target's equipment. He next advertises himself as a person of authority, ably skilled in solving that problem. In this step, he gains the trust of the target and obtains access to sensitive information.
If this reverse social engineering is performed well enough to convince the target, he often calls the attacker and asks for help. Answer B, C, D are incorrect. Person-to-Person social engineering works on the personal level. It can be classified as follows: Impersonation: In the impersonation social engineering attack, an attacker pretends to be someone else, for example, the employee's friend, a repairman, or a delivery person. In Person Attack: In this attack, the attacker just visits the organization and collects information. To accomplish such an attack, the attacker can call a victim on the phone, or might simply walk into an office and pretend to be a client or a new worker. Important User Posing: In this attack, the attacker pretends to be an important member of the organization. This attack works because there is a common belief that it is not good to question authority. Third-Party Authorization: In this attack, the attacker tries to make the victim believe that he has the approval of a third party. This works because people believe that most people are good and they are being truthful about what they are saying.
NEW QUESTION 4
John works as a professional Ethical Hacker. He has been assigned a project to test the security of www.we-are-secure.com. He performs Web vulnerability scanning on the We- are-secure server. The output of the scanning test is as follows: C.whisker.pl -h target_IP_address -- whisker / v1.4.0 / rain forest puppy / www.wiretrip.net -- = - = - = - = -
= = Host: target_IP_address = Server: Apache/1.3.12 (Win32) ApacheJServ/1.1 mod_ssl/2.6.4 OpenSSL/0.9.5a mod_perl/1.22 + 200 OK: HEAD /cgi-bin/printenv John recognizes /cgi-bin/printenv vulnerability ('Printenv' vulnerability) in the We_are_secure server. Which of the following statements about 'Printenv' vulnerability are true?
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
'Printenv' vulnerability allows an attacker to input specially crafted links and/or other malicious scripts. For example, http://www/cgi-bin/printenv/[removed]alert (An attacker can misuse it!)[removed] Since 'printenv' is just an example CGI script (It comes with various versions of the Apache Web server.) that has no real use and has its own problems, there is no problem in removing it. Answer B is incorrect. 'Printenv' does not maintain any log file of user activities.
NEW QUESTION 5
You work as a Database Administrator for XYZ CORP. The company has a multi-platform network. The company requires fast processing of the data in the database of the company so that answers to queries can be generated quickly. To provide fast processing, you have a conceptual idea of representing the dimensions of data available to a user in the data cube format. Which of the following systems can you use to implement your idea?
Answer: B
Explanation:
A multidimensional database management system (MDDBMS) implies the ability to rapidly process the data in the database so that answers to the queries can be generated quickly. A number of vendors provide products that use multidimensional databases. The approach behind this system is to manage that how data should be stored in the database, and depending upon that storage, how user interface should vary. Conceptually, an MDDBMS uses the idea of a data cube to represent the dimensions of data available to a user. For example, "sales" could be viewed in the dimensions of product model, geography, time, or some additional dimension. In this case, "sales" is known as the measure attribute of the data cube and the other dimensions are seen as feature attributes. Additionally, a database creator can define hierarchies and levels within a dimension (for example, state and city levels within a regional hierarchy). Answer C is incorrect. A federated database system is a type of meta-database management system (DBMS) that transparently integrates multiple autonomous database systems into a single federated database. The constituent databases are interconnected via a computer network, and may be geographically decentralized. Since the constituent database systems remain autonomous, a federated database system is a contrastable alternative to the (sometimes daunting) task of merging together several disparate databases. A federated database (or virtual database) is the fully-integrated, logical composite of all constituent databases in a federated database system. Answer A is incorrect. SYSDBA is a system privilege that allows a user to perform basic database administrative tasks, such as creating a database, altering a database, starting up and shutting down an Oracle instance, performing time- based recovery etc. The SYSDBA contains all system privileges with the ADMIN OPTION. It also contains the SYSOPER system privilege. Granting the SYSDBA system privilege to a user automatically adds him to the password file that is used to authenticate administrative users. Therefore, a user possessing the SYSDBA system privilege can connect to a database by using the password file authentication method. Answer D is incorrect. A hierarchical database is a database management system that implements the hierarchical data model. A hierarchical database system organizes data in a family tree structure such that each record has only one owner and the hierarchy is in a parent and child data segment. This implies that the record can have repeated information in a child segment. The best-known hierarchical DBMS is IMS.
NEW QUESTION 6
What are the different categories of PL/SQL program units?
Answer: BD
Explanation:
A named block is a PL/SQL block that Oracle stores in the database and can be called by name from any application. A named block is also known as a stored procedure. Named blocks can be called from any PL/SQL block. It has a declaration section, which is known as a header. The header may include the name of a block, type of the block, and parameter. The name and list of formal parameters are known as the signature of a subroutine. Once a named PL/SQL block is compiled, it gets permanently stored as p-code after compilation in the shared pool of the system global area. Therefore, the named block gets compiled only once. An anonymous block is a PL/SQL block that appears in a user's application and is neither named nor stored in the database. This block does not allow any mode of parameter. Anonymous block programs are effective in some situations. They are basically used when building scripts to seed data or perform one-time processing activities. They are also used when a user wants to nest activity in another PL/SQL block's execution section. Anonymous blocks are compiled each time they are executed.
NEW QUESTION 7
John works as a Network Administrator for We-are-secure Inc. The We-are-secure server is based on Windows Server 2003. One day, while analyzing the network security, he receives an error message that Kernel32.exe is encountering a problem. Which of the following steps should John take as a countermeasure to this situation?
Answer: CD
Explanation:
In such a situation, when John receives an error message revealing that Kernel32.exe is encountering a problem, he needs to come to the conclusion that his antivirus program needs to be updated, because Kernel32.exe is not a Microsoft file (It is a Kernel32.DLL file.). Although such viruses normally run on stealth mode, he should examine the process viewer (Task Manager) to see whether any new process is running on the computer or not. If any new process (malicious) is running on the server, he should exterminate that process. Answer A, B are incorrect. Since kernel.exe is not a real kernel file of Windows, there is no need to repair or download any patch for Windows Server 2003 from the Microsoft site to repair the kernel. Note: Such error messages can be received if the computer is infected with malware, such as Worm_Badtrans.b, Backdoor.G_Door, Glacier Backdoor, Win32.Badtrans.29020, etc.
NEW QUESTION 8
You work as the Network Administrator for XYZ CORP. The company has a Unix-based
network. You want to check the status of the printer and set its state. Which of the following Unix commands can you use to accomplish the task?
Answer: C
Explanation:
In Unix, the lpc command is used to check the status of the printer and set its state. Answer A is incorrect. In Unix, the banner command is used to print a large banner on the printer. Answer D is incorrect. In Unix, the lpr command is used to submit a job to the printer.
Answer B is incorrect. In Unix, the lpq command is used to show the contents of a spool directory for a given printer.
NEW QUESTION 9
You want to repeat the last command you entered in the bash shell. Which of the following commands will you use?
Answer: C
Explanation:
The history !! command shows the previously entered command in the bash shell. In the bash shell, the history command is used to view the recently executed commands. History is on by default. A user can turn off history using the command set +o history and turn it on using set -o history. An environment variable HISTSIZE is used to inform bash about how many history lines should be kept. The following commands are frequently used to view
and manipulate history: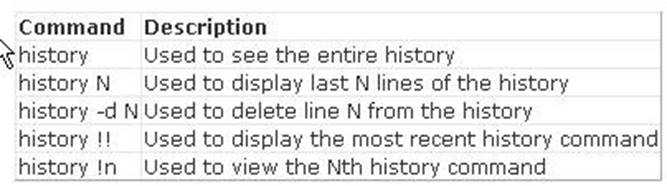
Answer B is incorrect. The history !# command shows the entire command line typed. Answer D is incorrect. The history !n command shows the nth command typed. Since n is equal to 1 in this command, the first command will be shown. Answer A is incorrect. It is not a valid command.
NEW QUESTION 10
Which of the following tools can be used to perform ICMP tunneling? (Choose two)
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Ptunnel and Itunnel are the tools that are used to perform ICMP tunneling. In ICMP tunneling, an attacker establishes a covert connection between two remote computers (a client and proxy), using ICMP echo requests and reply packets. ICMP tunneling works by injecting arbitrary data into an echo packet sent to a remote computer. The remote computer replies in the same manner, injecting an answer into another ICMP packet and sending it back. The client performs all communication using ICMP echo request packets, while the proxy uses echo reply packets. Normally, ICMP tunneling involves sending what appear to be ICMP commands but really they are the Trojan communications. Answer C is incorrect. WinTunnel is used to perform TCP tunneling. Answer D is incorrect. Ethereal is a network sniffer.
NEW QUESTION 11
You have detected what appears to be an unauthorized wireless access point on your network. However this access point has the same MAC address as one of your real access points and is broadcasting with a stronger signal. What is this called?
Answer: B
Explanation:
In the evil twin attack, a rogue wireless access point is set up that has the same MAC address as one of your legitimate access points. That rogue WAP will often then initiate a denial of service attack on your legitimate access point making it unable to respond to users, so they are redirected to the 'evil twin'. Answer A is incorrect. Blue snarfing is the process of taking over a PD Answer D is incorrect. A DOS may be used as part of establishing an evil twin, but this attack is not specifically for denial of service. Answer C is incorrect. While you must clone a WAP MAC address, the attack is not called WAP cloning.
NEW QUESTION 12
John works as a Network Administrator for Perfect Solutions Inc. The company has a Linux-based network. John is working as a root user on the Linux operating system. He wants to break a dat a.txt file, 200MB in size, into two files in which the size of the first file named data.txt.aa should be 150MB and that of the second file named data.txt.ab should be 50MB. To accomplish his task and to further delete the data.txt file, he enters the following command: split --verbose -b 150m data.txt data.txt. ; rm -vf data.txt Which of the following commands can John use to join the splitted files into a new data.txt file?
Answer: D
Explanation:
The cat data.txt.* command will display both the splitted files, and the > command will redirect the output into a new data.txt file.
NEW QUESTION 13
Which of the following attacks allows the bypassing of access control lists on servers or routers, and helps an attacker to hide? (Choose two)
Answer: CD
Explanation:
Either IP spoofing or MAC spoofing attacks can be performed to hide the identity in the network. MAC spoofing is a hacking technique of changing an assigned Media Access Control (MAC) address of a networked device to a different one. The changing of the assigned MAC address may allow the bypassing of access control lists on servers or routers, either hiding a computer on a network or allowing it to impersonate another computer. MAC spoofing is the activity of altering the MAC address of a network card. Answer A is incorrect. DNS cache poisoning is a maliciously created or unintended situation that provides data to a caching name server that did not originate from authoritative Domain Name System (DNS) sources. Once a DNS server has received such non-authentic datA, Caches it for future performance increase, it is considered poisoned, supplying the non-authentic data to the clients of the server. To perform a cache poisoning attack, the attacker exploits a flaw in the DNS software. If the server does not correctly validate DNS responses to ensure that they are from an authoritative source, the server will end up caching the incorrect entries locally and serve them to other users that make the same request. Answer B is incorrect. In a distributed denial of service (DDOS) attack, an attacker uses multiple computers throughout the network that has been previously infected. Such computers act as zombies and work together to send out bogus messages, thereby increasing the amount of phony traffic. The major advantages to an attacker of using a distributed denial-of-service attack are that multiple machines can generate more attack traffic than one machine, multiple attack machines are harder to turn off than one attack machine, and that the behavior of each attack machine can be stealthier, making it harder to track down and shut down. TFN, TRIN00, etc. are tools used for a DDoS attack.
NEW QUESTION 14
In a network, a data packet is received by a router for transmitting it to another network. For forwarding the packet to the other available networks, the router is configured with a static or a dynamic route. What are the benefits of using a static route?
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
Static routing is a data communication concept that describes a way to configure path selection of routers in computer networks. This is achieved by manually adding routes to the routing table. However, when there is a change in the network or a failure occurs between two statically defined nodes, traffic will not be rerouted. Static routing is beneficial in many ways: Precise control over the routes that a packet will take across the network Reduced load on the routers, as no complex routing calculations are required Reduced bandwidth use, as there is no excessive router traffic. Easy to configure in small networks Answer A is incorrect. This is a property of a dynamic route. A static route cannot choose the best path. It can only choose the paths that are manually entered.
When there is a change in the network or a failure occurs between two statically defined nodes, traffic will not be rerouted.
NEW QUESTION 15
What will happen if you write the following parameters in the web.xml file?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The
NEW QUESTION 16
You work as a Network Administrator for Tech Perfect Inc. The company has a TCP/IP based switched network. A root bridge has been elected in the switched network. You have installed a new switch with a lower bridge ID than the existing root bridge. What will happen?
Answer: A
Explanation:
The new switch starts advertising itself as the root bridge. It acts as it is the only bridge on the network. It has a lower Bridge ID than the existing root, so it is elected as the root bridge after the BPDUs converge and when all switches know about the new switch that it is the better choice. Answer B, C, D are incorrect. All these are not valid options, according to the given scenario.
NEW QUESTION 17
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security protocol for wireless local area networks (WLANs). It has two components, authentication and encryption. It provides security equivalent to wired networks for wireless networks. WEP encrypts data on a wireless network by using a fixed secret key. Which of the following statements are true about WEP?
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security protocol for wireless local area networks (WLANs). It has two components, authentication and encryption. It provides security equivalent to wired networks for wireless networks. WEP encrypts data on a wireless network by using a fixed secret key. WEP uses the RC4 encryption algorithm. The main drawback of WEP is that its Initialization Vector (IV) field is only 24 bits long. Many automated tools such as AirSnort are available for discovering WEP keys. Answer C is incorrect. WPA stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access. It is a wireless security standard. It provides better security than WEP (Wired Equivalent Protection). Windows Vista supports both WPA-PSK and WPA-EAP. Each of these is described as follows: WPA-PSK: PSK stands for Preshared key. This standard is meant for home environment. WPA-PSK requires a user to enter an 8- character to 63-character passphrase into a wireless client. The WPA converts the passphrase into a 256-bit key. WPA-EAP: EAP stands for Extensible Authentication Protocol. This standard relies on a back-end server that runs Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service for user authentication. Note: Windows Vista supports a user to use a smart card to connect to a WPA-EAP protected network.
NEW QUESTION 18
Which of the following records is the first entry in a DNS database file?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Start of Authority (SOA) record is the first record in any DNS database file. The SOA resource record includes the following fields: owner, TTL, class, type, authoritative server, refresh, minimum TTL, etc. Answer A is incorrect. Canonical Name (CNAME) is a resource record that creates an alias for the specified Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). It hides the implementation details of a network from the clients that are connected to the network. Answer D is incorrect. MX is a mail exchange resource record in the database file of a DNS server. It specifies a mail exchange server for a DNS domain name. Answer C is incorrect. SRV resource record is a DNS record that enables users to specify the location of servers for a specific service, protocol, and DNS domain. For example, if there are two servers in a domain, creating SRV records specifies which hosts serve as Web servers, and resolvers can then retrieve all the SRV resource records for the Web servers.
NEW QUESTION 19
The routing algorithm uses certain variables to create a metric of a path. It is the metric that actually determines the routing path. In a metric, which of the following variables is used to define the 'largest size' of a message that can be routed?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The routing algorithm uses certain variables to create a metric of a path. It is the metric that is actually used for path determination. Variables that are used to create a metric of a path are as follows: Hop count: It is the total number of routers that a data packet goes through to reach its destination. Cost: It is determined by the administrator or calculated by the router. Bandwidth: It is defined as the bandwidth that the link provides. Maximum transmission unit (MTU): It is the largest message size that a link can route. Load: It states the amount of work the CPU has to perform and the number of packets the CPU needs to analyze and make calculations on.
NEW QUESTION 20
......
P.S. Dumps-files.com now are offering 100% pass ensure GSNA dumps! All GSNA exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.dumps-files.com/files/GSNA/ (368 New Questions)