
Want to know Testking HPE6-A70 Exam practice test features? Want to lear more about HP Implementing Aruba WLAN (IAW) 8.4 certification experience? Study Download HP HPE6-A70 answers to Replace HPE6-A70 questions at Testking. Gat a success with an absolute guarantee to pass HP HPE6-A70 (Implementing Aruba WLAN (IAW) 8.4) test on your first attempt.
Free HPE6-A70 Demo Online For HP Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which task can an Aruba Air Monitor (AM) perform?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 2
A network administrator examines a list of 2.4GHz clients with low performance in the Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. Which property for a client should pose a concern as a potential performance issue?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
Exhibit 2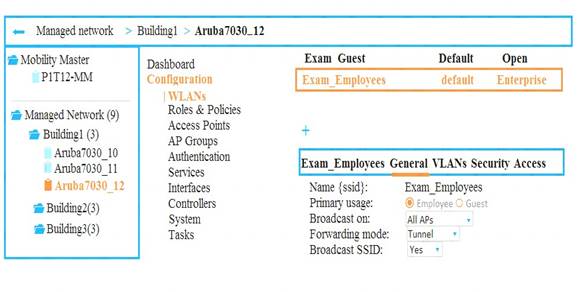
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution and needs a new WLAN for the corporate campus. A network administrator completes the creation of this WLAN, as shown in Exhibit 1. When the administrator tries to test a connection to the WLAN in various locations, the WLAN sometimes shows up in the list of WLANs on the client but sometimes does not. The administrator can see the WLAN in the list, as shown in Exhibit 2.
What is the error?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 4
A network administrator configures an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution to provide wireless access to employees. The solution must meet these criteria: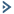 Authenticate users to a network RADIUS server
Authenticate users to a network RADIUS server Enforce different Aruba firewall rules based on the user department
Enforce different Aruba firewall rules based on the user department
How can the administrator meet these criteria in the simplest way?
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 5
Which Aruba controller supports a maximum of 512 APs?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 6
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with a WLAN that assigns users to VLANs 10–19. The company wants the Aruba solution to act at Layer 3 to route wireless user traffic.
What must network administrators configure to permit the solution to forward traffic correctly?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
What is a reason for a company to choose to deploy an Aruba 7024 Mobility Controller (MC) rather than an Aruba 7010 MC?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 8
What is a valid way to deploy an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. There is a hardware issue with the MM appliance, and, as result, all connectivity is lost between the appliance and the network. The network manager is concerned about how this will impact licensing.
How will the Mobility Controller (MC) be affected?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 10
An AP operates on channel 6. Which device causes the most significant and consistent interference with the signal?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 11
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution that runs ArubaOS 8 and uses the default AirMatch and Client Match settings. The ARM profile has been disabled for 5GHz radios. How are channel and transmit power settings managed for these radios?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 12
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. Where can network administrators look to monitor the health status of all controllers, APs, and clients?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit.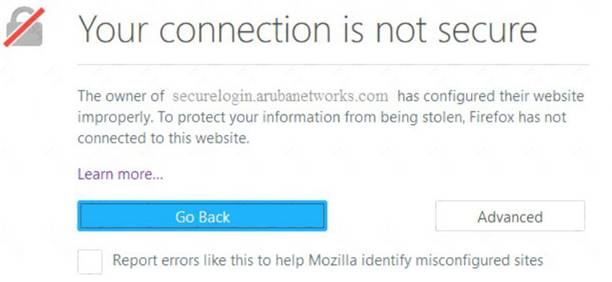
A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with a guest WLAN. During the captive portal redirection, users who access a non-HTTPS Website see the error shown in the exhibit.
How can a network administrator prevent this error?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 14
Refer to the exhibit.
The exhibit shows output from a Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. What is a valid reason for the administrator to click the akamai square under applications?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 15
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM). The MM will manage 50 Mobility Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 680 APs, and 10 Virtual Mobility Controllers (VMCs) that will control a total of 160 APs.
How many MM licenses does the company require?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Starting with ArubaOS 8.0.1, the MM license is required to terminate devices (controllers or APs) on Mobility Master. If the Mobility Master does not have sufficient MM licenses and an AP fails to obtain a license, that AP can get an IP address and connect to its controller, but will not broadcast an SSID.
NEW QUESTION 16
How can network administrator provide high availability for APs deployed in an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based architecture?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 17
Refer to the exhibit.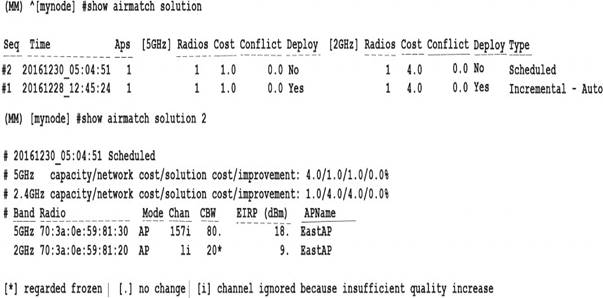
An Aruba solution uses AirMatch with the default AirMatch profile settings. A network administrator sees that a scheduled optimization was completed, but a plan was not deployed.
Based on the exhibit, why did this occur?
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 18
What is the minimum space between channels in the 2.4GHz range to prevent overlap?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 19
An Aruba solution has a WLAN that uses WPA2-Personal security. How are encryption keys dynamically managed for the wireless users?
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 20
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM) solution with two MM nodes. The MM solution will manage 10 Mobility Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 400 APs.
How should the network administrator install the AP licenses?
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 21
A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. A network administrator wants to monitor the types of applications in use in the wireless network.
Which dashboard page in the MM interface should the administrator visit?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 22
Refer to the exhibit.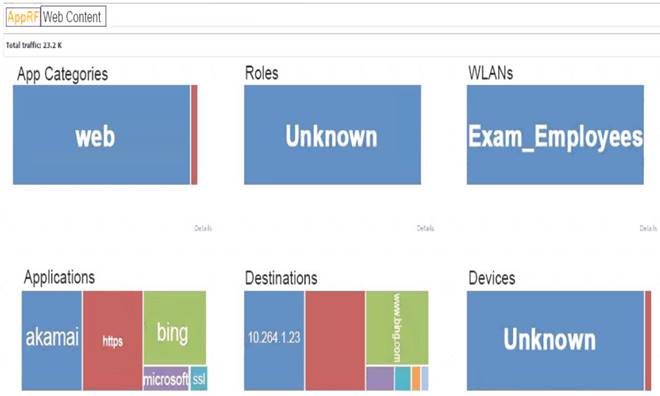
The exhibit shows output from a Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. What is a valid reason for the administrator to click the akamai square under applications?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 23
An Aruba solution has a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. How are encryption keys dynamically managed for the wireless users?
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 24
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1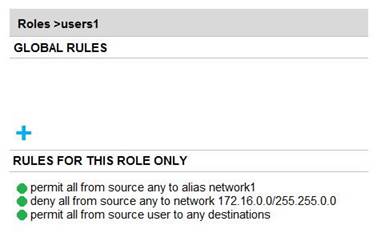
Exhibit 2
A company has an Aruba solution. Client 1 is assigned to the users1 role, and client 2 is assigned to the users2 role. The exhibits show current firewall rules for those roles. The network1 alias used to be 10.1.1.0/24, but the network administrator now changes the network1 alias to 172.16.1.0/24. Client 1 and Client 2 both send a packet destined to 172.16.1.10.
How does the firewall handle these packets?
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 25
......
Recommend!! Get the Full HPE6-A70 dumps in VCE and PDF From Thedumpscentre.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.thedumpscentre.com/HPE6-A70-dumps/ (New 131 Q&As Version)