
Act now and download your ISC2 SSCP test today! Do not waste time for the worthless ISC2 SSCP tutorials. Download Latest ISC2 System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) exam with real questions and answers and begin to learn ISC2 SSCP with a classic professional.
Free SSCP Demo Online For ISC2 Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
In a hierarchical PKI the highest CA is regularly called Root CA, it is also referred to by which one of the following term?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Reference: Arsenault, Turner, Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure: Roadmap, Chapter "Terminology".
Also note that sometimes other terms such as Certification Authority Anchor (CAA) might be used within some government organization, Top level CA is another common term to indicate the top level CA, Top Level Anchor could also be used.
NEW QUESTION 2
This baseline sets certain thresholds for specific errors or mistakes allowed and the amount of these occurrences that can take place before it is considered suspicious?
Answer: C
Explanation:
Organizations usually forgive a particular type, number, or pattern of violations, thus permitting a predetermined number of user errors before gathering this data for analysis. An organization attempting to track all violations, without sophisticated statistical computing ability, would be unable to manage the sheer quantity of such data. To make a violation listing effective, a clipping level must be established.
The clipping level establishes a baseline for violation activities that may be normal user errors. Only after this baseline is exceeded is a violation record produced. This solution is particularly effective for small- to medium-sized installations. Organizations with large-scale computing facilities often track all violations and use statistical routines to cull out the minor infractions (e.g., forgetting a password or mistyping it several times).
If the number of violations being tracked becomes unmanageable, the first step in correcting the problems should be to analyze why the condition has occurred. Do users understand how they are to interact with the computer resource? Are the rules too difficult to follow? Violation tracking and analysis can be valuable tools in assisting an organization to develop thorough but useable controls. Once these are in place and records are produced that accurately reflect serious violations, tracking and analysis become the first line of defense. With this procedure, intrusions are discovered before major damage occurs and sometimes early enough to catch the perpetrator. In addition, business protection and preservation are strengthened.
The following answers are incorrect:
All of the other choices presented were simply detractors. The following reference(s) were used for this question:
Handbook of Information Security Management
NEW QUESTION 3
Which of the following is true related to network sniffing?
Answer: A
Explanation:
The following answers are incorrect: Sniffers alter the source address of a computer to disguise and exploit weak authentication methods. IP Spoofing is a network-
based attack, which involves altering the source address of a computer to disguise the attacker and exploit weak authentication methods.
Sniffers take over network connections. Session Hijacking tools allow an attacker to take over network connections, kicking off the legitimate user or sharing a login.
Sniffers send IP fragments to a system that overlap with each other. Malformed Packet attacks are a type of DoS attack that involves one or two packets that are formatted in an unexpected way. Many vendor product implementations do not take into account all variations of user entries or packet types. If software handles such errors poorly, the system may crash when it receives such packets. A classic example of this type of attack involves sending IP fragments to a system that overlap with each other (the fragment offset values are incorrectly set. Some unpatched Windows and Linux systems will crash when the encounter such packets.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, MICKI, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th Edition, Volume 2, Auerbach, NY, NY 2001, Chapter 22, Hacker Tools and Techniques by Ed Skoudis.
ISC2 OIG, 2007 p. 137-138, 419
NEW QUESTION 4
Which of the following is true about link encryption?
Answer: C
Explanation:
In link encryption, each entity has keys in common with its two neighboring nodes in the transmission chain.
Thus, a node receives the encrypted message from its predecessor, decrypts it, and then re-encrypts it with a new key, common to the successor node. Obviously, this mode does not provide protection if anyone of the nodes along the transmission path is compromised.
Encryption can be performed at different communication levels, each with different types of protection and implications. Two general modes of encryption implementation are link encryption and end-to-end encryption.
Link encryption encrypts all the data along a specific communication path, as in a satellite link, T3 line, or telephone circuit. Not only is the user information encrypted, but the header, trailers, addresses, and routing data that are part of the packets are also encrypted. The only traffic not encrypted in this technology is the data link control messaging information, which includes instructions and parameters that the different link devices use to synchronize communication methods. Link encryption provides protection against packet sniffers and eavesdroppers.
In end-to-end encryption, the headers, addresses, routing, and trailer information are not encrypted, enabling attackers to learn more about a captured packet and where it is headed.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (pp. 845-846). McGraw-Hill.
And:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 132).
NEW QUESTION 5
In telephony different types of connections are being used. The connection from the phone company's branch office to local customers is referred to as which of the following choices?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Transmission on fiber optic wire requires repeating at distance intervals. The glass fiber requires more protection within an outer cable than copper. For these reasons and because the installation of any new wiring is labor-intensive, few communities yet have fiber optic wires or cables from the phone company's branch office to local customers (local loop).
In telephony, a local loop is the wired connection from a telephone company's central office
in a locality to its customers' telephones at homes and businesses. This connection is usually on a pair of copper wires called twisted pair. The system was originally designed for voice transmission only using analog transmission technology on a single voice channel. Today, your computer's modem makes the conversion between analog signals and digital signals. With Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), the local loop can carry digital signals directly and at a much higher bandwidth than they do for voice only.
Local Loop diagram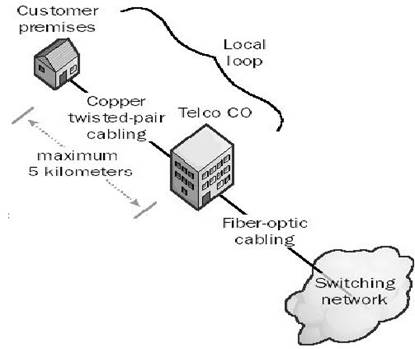
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Image from: http://www.thenetworkencyclopedia.com/entry/local-loop/
The following are incorrect answers:
New loop This is only a detractor and does not exist
Loopback In telephone systems, a loopback is a test signal sent to a network destination that is returned as received to the originator. The returned signal may help diagnose a
problem.
Ingenious loop This is only a detractor and does not exist
Reference(s) used for this question: http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/local-loop
and
STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 14.
NEW QUESTION 6
What is called a system that is capable of detecting that a fault has occurred and has the ability to correct the fault or operate around it?
Answer: C
Explanation:
A fault-tolerant system is capable of detecting that a fault has occurred and has the ability to correct the fault or operate around it. In a fail-safe system, program execution is terminated, and the system is protected from being compromised when a hardware or software failure occurs and is detected. In a fail-soft system, when a hardware or software failure occurs and is detected, selected, non-critical processing is terminated. The term failover refers to switching to a duplicate "hot" backup component in real-time when a hardware or software failure occurs, enabling processing to continue.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 5: Security Architecture and Models (page 196).
NEW QUESTION 7
What is a packet sniffer?
Answer: D
Explanation:
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation.
NEW QUESTION 8
Compared to RSA, which of the following is true of Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC)?
Answer: D
Explanation:
The following answers are incorrect: It has been mathematically proved to be less secure. ECC has not been proved to be more or less secure than RSA. Since ECC is newer than RSA, it is considered riskier by some, but that is just a general assessment, not based on mathematical arguments.
It has been mathematically proved to be more secure. ECC has not been proved to be more or less secure than RSA. Since ECC is newer than RSA, it is considered riskier by some, but that is just a general assessment, not based on mathematical arguments.
It is believed to require longer key for equivalent security. On the contrary, it is believed to require shorter keys for equivalent security of RSA.
Shon Harris, AIO v5 pg719 states:
"In most cases, the longer the key, the more protection that is provided, but ECC can provide the same level of protection with a key size that is shorter that what RSA requires"
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question: ISC2 OIG, 2007 p. 258
Shon Harris, AIO v5 pg719
NEW QUESTION 9
What is the difference between Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Capability Tables?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Capability tables are used to track, manage and apply controls based on the object and rights, or capabilities of a subject. For example, a table identifies the object, specifies access rights allowed for a subject, and permits access based on the user's
posession of a capability (or ticket) for the object. It is a row within the matrix.
To put it another way, A capabiltiy table is different from an ACL because the subject is bound to the capability table, whereas the object is bound to the ACL.
CLEMENT NOTE:
If we wish to express this very simply:
Capabilities are attached to a subject and it describe what access the subject has to each of the objects on the row that matches with the subject within the matrix. It is a row within the matrix.
ACL's are attached to objects, it describe who has access to the object and what type of access they have. It is a column within the matrix.
The following are incorrect answers:
"Access control lists are subject-based whereas capability tables are object-based" is incorrect.
"Capability tables are used for objects whereas access control lists are used for users" is incorrect.
"They are basically the same" is incorrect. References used for this question:
CBK, pp. 191 - 192
AIO3 p. 169
NEW QUESTION 10
To understand the 'whys' in crime, many times it is necessary to understand MOM. Which of the following is not a component of MOM?
Answer: B
Explanation:
To understand the whys in crime, many times it is necessary to understand the Motivations, Opportunities, and Means (MOM). Motivations are the who and why of a crime. Opportunities are the where and when of a crime, and Means pertains to the capabilities a criminal would need to be successful. Methods is not a component of MOM.
NEW QUESTION 11
What works as an E-mail message transfer agent?
Answer: A
Explanation:
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) works as a message transfer agent. Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2001, Page 821.
NEW QUESTION 12
Of the following, which is NOT a specific loss criteria that should be considered while developing a BIA?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Although a loss of skilled workers knowledge would cause the company a great loss, it is not identified as a specific loss criteria. It would fall under one of the three other criteria listed as distracters.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 9: Disaster Recovery and Business continuity (page 598).
NEW QUESTION 13
Who should DECIDE how a company should approach security and what security measures should be implemented?
Answer: A
Explanation:
They are responsible for security of the organization and the protection of its
assets.
The following answers are incorrect because :
Data owner is incorrect as data owners should not decide as to what security measures should be applied.
Auditor is also incorrect as auditor cannot decide as to what security measures should be applied.
The information security specialist is also incorrect as they may have the technical knowledge of how security measures should be implemented and configured , but they should not be in a position of deciding what measures should be applied.
Reference : Shon Harris AIO v3 , Chapter-3: Security Management Practices , Page : 51.
NEW QUESTION 14
A DMZ is also known as a
Answer: A
Explanation:
This is another name for the demilitarized zone (DMZ) of a network.
"Three legged firewall" is incorrect. While a DMZ can be implemented on one leg of such a device, this is not the best answer.
"A place to attract hackers" is incorrect. The DMZ is a way to provide limited public access to an organization's internal resources (DNS, EMAIL, public web, etc) not as an attractant for hackers.
"Bastion host" is incorrect. A bastion host serves as a gateway between trusted and untrusted network.
References: CBK, p. 434
AIO3, pp. 495 - 496
NEW QUESTION 15
What is the main problem of the renewal of a root CA certificate?
Answer: B
Explanation:
The main task here is the authentic distribution of the new root CA certificate as new trust anchor to all the PKI participants (e.g. the users).
In some of the rollover-scenarios there is no automatic way, often explicit assignment of trust from each user is needed, which could be very costly.
Other methods make use of the old root CA certificate for automatic trust establishment (see PKIX-reference), but these solutions works only well for scenarios with currently valid root CA certificates (and not for emergency cases e.g. compromise of the current root CA certificate).
The rollover of the root CA certificate is a specific and delicate problem and therefore are often ignored during PKI deployment.
Reference: Camphausen, I.; Petersen, H.; Stark, C.: Konzepte zum Root CA Zertifikatswechsel, conference Enterprise Security 2002, March 26-27, 2002, Paderborn; RFC 2459 : Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and CRL Profile.
NEW QUESTION 16
What does the simple security (ss) property mean in the Bell-LaPadula model?
Answer: A
Explanation:
The ss (simple security) property of the Bell-LaPadula access control model states that reading of information by a subject at a lower sensitivity level from an object at a higher sensitivity level is not permitted (no read up).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 5: Security Architectures and Models (page 202).
NEW QUESTION 17
The standard server port number for HTTP is which of the following?
Answer: B
Explanation:
HTTP is Port 80.
Reference: MAIWALD, Eric, Network Security: A Beginner's Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne Media, 2001, page 135.
NEW QUESTION 18
Which of the following is not a security goal for remote access?
Answer: D
Explanation:
An automated login function for remote users would imply a weak authentication, thus certainly not a security goal.
Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, Micki, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th edition, volume 2, 2001, CRC Press, Chapter 5: An Introduction to Secure Remote Access (page 100).
NEW QUESTION 19
Which one of the following represents an ALE calculation?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) is the dollar amount that would be lost if there was a loss of an asset. Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) is an estimated possibility of a threat to an asset taking place in one year (for example if there is a change of a flood
occuring once in 10 years the ARO would be .1, and if there was a chance of a flood occuring once in 100 years then the ARO would be .01).
The following answers are incorrect:
gross loss expectancy x loss frequency. Is incorrect because this is a distractor.
actual replacement cost - proceeds of salvage. Is incorrect because this is a distractor. asset value x loss expectancy. Is incorrect because this is a distractor.
NEW QUESTION 20
The major objective of system configuration management is which of the following?
Answer: B
Explanation:
A major objective with Configuration Management is stability. The changes to the system are controlled so that they don't lead to weaknesses or faults in th system.
The following answers are incorrect:
system maintenance. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. Configuration Management does control the changes to the system but it is not as important as the overall stability of the system.
system operations. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, the overall stability of the system is much more important.
system tracking. Is incorrect because while tracking changes is important, it is not the best answer. The overall stability of the system is much more important.
NEW QUESTION 21
Why are coaxial cables called "coaxial"?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Coaxial cable is called "coaxial" because it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
The outer channel serves as a ground. Many of these cables or pairs of coaxial tubes can be placed in a single outer sheathing and, with repeaters, can carry information for a great distance.
Source: STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 14.
NEW QUESTION 22
Which of the following protocols operates at the session layer (layer 5)?
Answer: A
Explanation:
Remotre Procedure Call (RPC) is the only of the above choices to operate at the session layer (layer 5).
All of the other answers were wrong. LPD operates at layer 7
SPX operates at layer 4
IGMP operates at layer 3.
Reference:
WALLHOFF, John, CBK#2 Telecommunications and Network Security (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 1).
NEW QUESTION 23
......
100% Valid and Newest Version SSCP Questions & Answers shared by Certshared, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.certshared.com/exam/SSCP/ (New 1074 Q&As)